 Simulation of Kelvin-Helmholtz waves in Earth's magnetosphere. (S. Kavosi/J. Raeder/UNH)
Simulation of Kelvin-Helmholtz waves in Earth's magnetosphere. (S. Kavosi/J. Raeder/UNH)
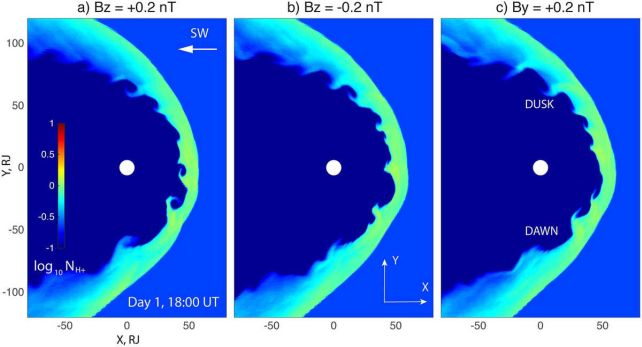
Giant waves have been found swirling in the plasma at the boundary of Jupiter's magnetosphere, scientists have found.
Data from Juno suggests the Jupiter probe regularly dips through these waves, invisible to the naked eye, as it orbits the giant planet. The discovery helps astronomers understand how mass and energy is transferred from the solar wind to the Jovian planetary environment.
They've been observed at the boundary of Earth's magnetosphere as well, not to mention near Saturn. The conditions under which they form are not well understood, though, so finding them in Jupiter's vicinity could yield some clues.
"Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are a fundamental physical process that occurs when solar and stellar winds interact with planetary magnetic fields across our Solar System and throughout the universe," says astrophysicist Jake Montgomery of the University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) and the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI).
"Juno observed these waves during many of its orbits, providing conclusive evidence that Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities play an active role in the interaction between the solar wind and Jupiter."
The environment around Jupiter is a pretty wild place. Jupiter's magnetic field is huge, and its volcanic moon Io is a powerful source of charged particles, constantly belching material into a huge plasma torus that circles the huge gas giant. Jupiter's moon Ganymede generates a relatively strong magnetic field of its own.
The discovery of Kelvin-Helmholtz waves at Jupiter's magnetopause will help astronomers understand the complex interplays taking place in Jovian space.
"Juno's extensive time near Jupiter's magnetopause has enabled detailed observations of phenomena such as Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities in this region," says astrophysicist Robert Ebert of SwRI and UTSA.
"This solar wind interaction is important as it can transport plasma and energy across the magnetopause, into Jupiter's magnetosphere, driving activity within that system."
The waves were not detected in many of Juno's magnetopause crossings, and this has important implications too. Studying the conditions under which these waves are generated could help figure out how they form, which has broader implications.
For example, wrinkles have been detected at the heliopause – the boundary between the solar wind and interstellar space, far out beyond the planets. Understanding what drives Kelvin-Helmholtz waves could help identify the dynamics at play at the Solar System's border.
The research has been published in Geophysical Research Letters.









0 Comments